Elliott Wave Theory พยายามระบุการเคลื่อนไหวของราคาที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำในตลาดการเงินและจัดประเภทไว้ในรูปแบบที่มีความหมายซึ่งสามารถกลายเป็นเครื่องมือที่เชื่อถือได้สำหรับการคาดการณ์ราคาในอนาคต หลักการพื้นฐานคือการเคลื่อนไหวของราคาจะเกิดขึ้นผ่านการสลับที่ไม่มีที่สิ้นสุดระหว่างแนวโน้มและรอบการแก้ไขขณะที่สร้างผลกระทบนี้ในช่วงเวลาที่สัมพันธ์กัน ( เศษส่วน )
รูปแบบราคา Elliott Wave (EW) แบ่งออกเป็นคลื่นแรงจูงใจ (เช่นการเคลื่อนไหวของราคาที่เริ่มต้นความคืบหน้าในทิศทางเดียวและดังนั้นจึงสร้างแนวโน้ม) และคลื่นแก้ไข (เช่นการเคลื่อนไหวของราคาที่เป็นปฏิกิริยาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการเคลื่อนไหวการตั้งค่าแนวโน้มก่อนหน้า) คลื่นที่ถูกต้องจะพยายามที่จะย้อนกลับหรือยกเลิกการเคลื่อนไหวที่เกิดจากคลื่นแรงจูงใจก่อนหน้า
วิธีใช้คู่มือนี้
คู่มืออ้างอิง EW นี้ให้การวาดภาพในอุดมคติสำหรับแต่ละรูปแบบ EW รวมถึงการสร้างภาพของความสัมพันธ์ขนาดคลื่นภายในที่สำคัญที่สุด รูปภาพจะเน้นที่การถอยกลับของคลื่นที่พบมากที่สุดและเป้าหมายส่วนขยายเป็นสีแดงตามด้วยเป้าหมายที่พบบ่อยที่สุดถัดไปในสีส้มตามด้วยเป้าหมายที่พบได้น้อยที่สุดในสีเทา
แนวคิดสำคัญที่ต้องจำไว้ก่อนนำไปใช้นับ EW
คลื่นดีกรี
Elliott Waves มีการระบุไว้ในองศาที่แตกต่างกันซึ่งซ้อนกันภายในเนื่องจากลักษณะเศษส่วนของการเคลื่อนไหวของราคา โปรดดูซอฟต์แวร์การวาดรูป Elliott Wave ของคุณสำหรับชื่อและสัญลักษณ์ที่เหมาะสมที่ใช้สำหรับการศึกษาระดับปริญญาที่กำหนดไว้อย่างเป็นทางการในแต่ละระดับ หรือคุณอาจกำหนดป้ายกำกับองศาที่แตกต่างด้วยป้ายชื่อสีต่างกันในแผนภูมิของคุณ
การสลับ(“ คาดหวังความแตกต่างในนิพจน์ถัดไปของรูปแบบที่คล้ายกัน”):
รูปแบบ EW มีแนวโน้มที่จะสร้างการเปลี่ยนแปลงภายใน นี่คือการสะท้อนความโน้มเอียงทั่วไปของธรรมชาติที่มีต่อสมดุลแบบไดนามิก ต่อไปนี้เป็นรายการของการเกิดขึ้นหลักของการสลับ:
การสลับของคลื่นแก้ไข:
- หากคลื่น 2 มีความคมชัด (เช่นคดเคี้ยวไปมาหรือซิกแซกขยาย) และลึก (เช่นลึกลงไปในความรู้สึกว่ามัน retraces คลื่นก่อนหน้า 1) แล้วคลื่น 4 จะเป็นไปได้ด้านข้าง (แบนการรวมกันหรือสามเหลี่ยม) และ ตื้น ๆ ที่สัมพันธ์กับคลื่น 3 เช่นเดียวกับในสิ่งที่ตรงกันข้าม แต่เป็นเรื่องธรรมดาน้อย นี่เป็นเพราะสามเหลี่ยม (ซึ่งปรากฏระหว่างคลื่น 4 ในคลื่นแรงจูงใจเท่านั้น) จึงถือเป็นการสลับไปยังรูปแบบการแก้ไขอื่น ๆ ทั้งหมด นั่นหมายความว่าแม้ว่าคลื่นที่ 2 เป็นการแก้ไขด้านข้างแบบตื้นสามเหลี่ยมก็ยังสามารถปรากฏในคลื่นที่ 4 แต่มีโอกาสน้อยกว่า
- การสลับเกิดขึ้นในแง่ของความซับซ้อนของคลื่น หากการแก้ไขที่ซับซ้อนที่ใหญ่กว่าที่อาจเกิดขึ้นเริ่มต้นง่ายๆในตอนแรกคาดว่าจะมีความซับซ้อนเพิ่มขึ้นในระหว่างการแก้ไขส่วนต่อไปนี้ (เช่นซับซ้อนที่ซับซ้อนมากที่สุด) ย้อนกลับยังสามารถนำไปใช้ (เช่นซับซ้อนที่สุดซับซ้อนง่าย ๆ ) แต่มันหายากมากขึ้น
การสลับของโมทีฟคลื่น:
- ถ้าคลื่น 1 สั้นคลื่นก็น่าจะยืดออกและคลื่น 5 น่าจะสั้นอีกครั้ง หากคลื่นที่ 1 ขยายออกไปคลื่นที่ 3 และ 5 จะไม่ขยายออกไป หากไม่มีการยืดคลื่น 1 หรือ 3 คลื่นอาจเป็น 5 หากคลื่น 3 ยาวมากและมีคลื่นมากเกินไปคลื่นจะมีความเสี่ยงมากขึ้นที่จะถูกตัดทอนอีก 5
สัดส่วนที่สมดุล (“ The Right Look”):
เป็นสิ่งสำคัญที่คลื่นภายในลำดับ 5 คลื่นหรือ 3 คลื่นแสดงสัดส่วนที่สมดุลกัน ... ไม่เพียง แต่ในแง่ของขนาด / ขนาด (ซึ่งโดยทั่วไปสามารถตรวจสอบโดย Fibonacci retracement และอัตราส่วนการขยาย) แต่ในแง่ของระยะเวลา การทรงตัวนี้สามารถเกิดขึ้นได้ผ่านการสับเปลี่ยนและ / หรือผ่านความเท่าเทียมกัน
ลองพิจารณาตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้สำหรับ 'ดุลยภาพผ่านการเปลี่ยนแปลง' : แรงกระตุ้นแสดงคลื่นลึกและระยะสั้นแบบคลาสสิก 2 บวกกับคลื่นตื้น ๆ แต่ยาวเป็นเวลา 4 ความยาวของคลื่น 4 อยู่ในสมดุลกับความลึก ของคลื่น 2 ในขณะที่ความตื้นของคลื่น 4 อยู่ในสมดุลกับธรรมชาติที่สั้นของคลื่น 2 จึงสร้างสมดุลผ่านการสลับ
ความต้องการความสมดุลแบบเดียวกันนั้นใช้กับคลื่นแรงจูงใจใด ๆ ในลำดับ 5 คลื่น (เช่น 1,3 และ 5) อย่างไรก็ตามข้อยกเว้นจะเป็นคลื่นที่อาจขยายเพิ่มเติมภายในลำดับ มันสามารถ / จะมีขนาดใหญ่กว่าในแง่ของขนาดและเวลามากกว่าอีกสี่คลื่น แต่คลื่นย่อย (ภายในคลื่นขยาย) จะต้องแสดงความสมดุลซึ่งกันและกัน คลื่นที่ขยายจะแสดงความเกี่ยวข้องกับคลื่นอื่น ๆ ของลำดับโดยมุมของการเคลื่อนไหวของราคาโดยรวม (นั่นเป็นสาเหตุที่คลื่นแรงกระตุ้นที่ถูกกระตุ้นนั้นเคลื่อนที่ค่อนข้างเรียบร้อยภายในเส้นคู่ขนานส่วนใหญ่เวลาแม้ว่าคลื่นหนึ่งคลื่นจะยืดออก)
พิจารณาต่อไปนี้เป็นตัวอย่างสำหรับ 'ความสมดุลผ่านความเสมอภาคและการสลับ' คลื่น 1 และ 5 ของลำดับอิมพัลส์นั้นมีขนาดและระยะเวลาเท่ากัน (ความเท่าเทียมกัน) ในขณะที่คลื่น 3 จะถูกขยาย (สลับกับคลื่น 1 และ 5)
สัญญาณเตือนภัยควรจะดับลงเมื่อคลื่นที่มีศักยภาพ 4 เริ่มเติบโตจากสัดส่วนในแง่ของขนาดและระยะเวลาเมื่อเทียบกับคลื่นอื่น ๆ ในระดับเดียวกัน
การไม่สนใจปัจจัยสัดส่วนที่สมดุลระหว่างการนับคลื่น รูปแบบที่ไม่เหมาะสมและผิดรูปควรถูกสอบสวนอย่างจริงจัง
'รูปลักษณ์ที่ถูกต้อง' อาจไม่ปรากฏในทุกระดับของเทรนด์พร้อมกันดังนั้นจึงเป็นการดีที่สุดที่จะมุ่งเน้นไปที่องศาที่ชัดเจนที่สุด
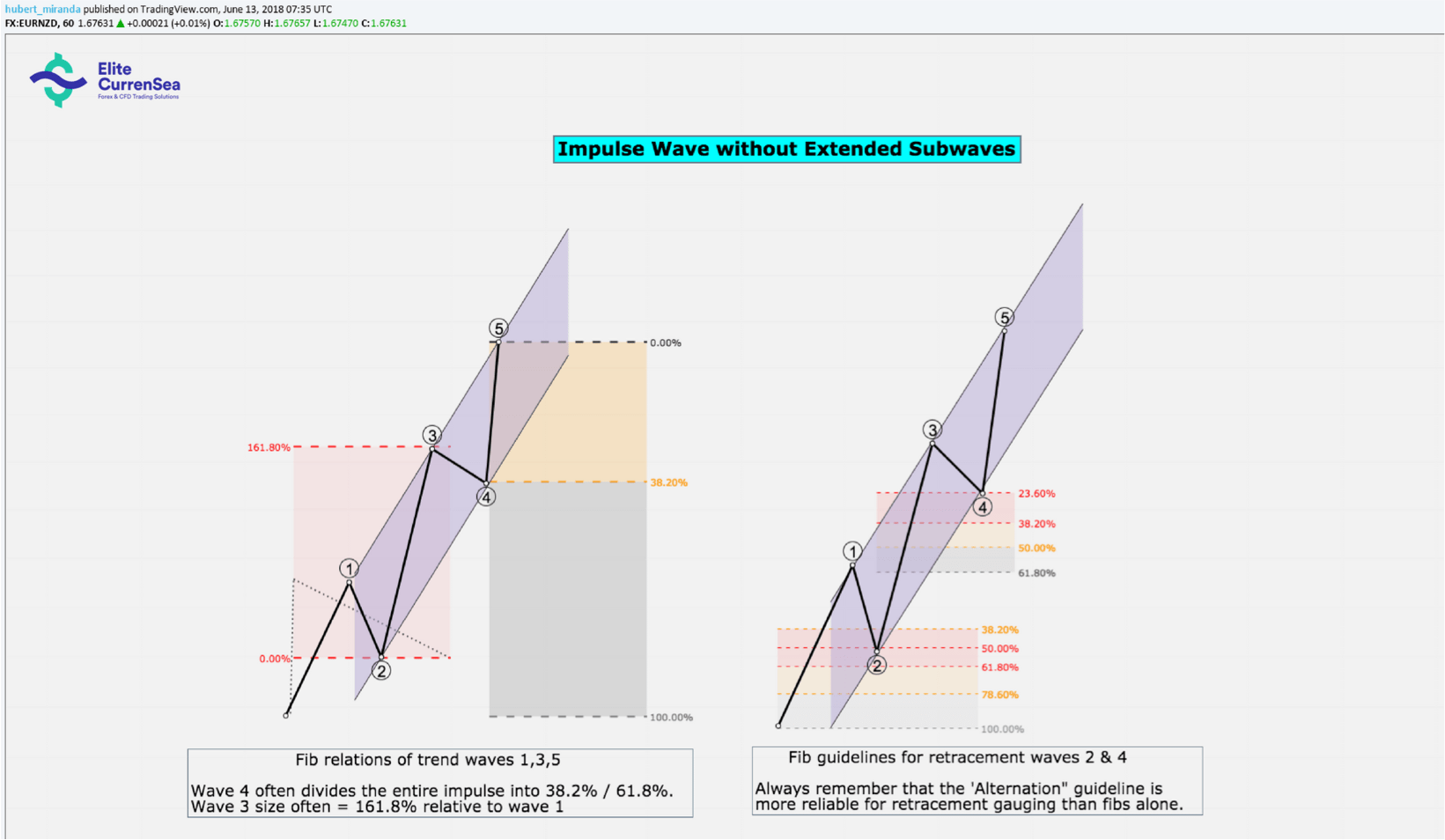
Motive Wave: IMPULSE
หมายเหตุ: เปอร์เซ็นต์ในข้างต้นสำหรับเป้าหมายการขยาย Fibonacci ถูกดึงจากจุดเริ่มต้นของคลื่น แต่อัตราส่วนจะขึ้นอยู่กับขนาดของคลื่นเคลื่อนที่ก่อนหน้า (เช่นเป้าหมายของ 3 จะสัมพันธ์กับขนาดของคลื่น 1 เป้าหมายของคลื่น 5 มีความสัมพันธ์กับขนาดของคลื่น 3
- แรงกระตุ้นประกอบด้วย 5 คลื่นภายใน
- คลื่นที่ 1 และ 5 จะต้องมีแรงกระตุ้นหรือเส้นทแยงมุมเสมอ
- Wave 3 ต้องเป็นแรงกระตุ้นเสมอ (เช่นไม่สามารถเป็นแนวทแยงมุม)
- Wave 3 จะต้องไม่สั้นที่สุด (ในรูปของเปอร์เซ็นต์กำไร / ขาดทุน) ตามลำดับ
- Wave 2 เป็นรูปแบบที่ถูกต้องเสมอและต้องไม่ย้อนกลับมากกว่า 100% ของ wave 1
- Wave 2 สามารถแก้ไขรูปแบบใดก็ได้ยกเว้นรูปสามเหลี่ยม (แต่อาจเป็นรูปแบบที่ซับซ้อน (wxy หรือ wxyz) ที่ลงท้ายด้วยรูปสามเหลี่ยม)
- Wave 4 จะต้องไม่เข้าสู่อาณาเขตราคาของ Wave 1
- Wave 4 ต้องเป็นรูปแบบการแก้ไข (ใด ๆ ) เสมอ
แนวทาง:
- คลื่น 2 และ 4 มีแนวโน้มที่จะสร้างการสลับกันระหว่างกัน (ดังที่อธิบายไว้ในบทนำของคู่มือนี้)
- โดยปกติแล้วคลื่น 2 จะกลับไปที่ระดับ 1 ของคลื่นลึกกว่าคลื่น 4 ซึ่งสัมพันธ์กับคลื่น 3
- Wave 2 พัฒนาโดยทั่วไปว่าเป็นรูปแบบการแก้ไขอย่างง่าย (เช่นคดเคี้ยวไปมาหรือสองครั้ง / ซิกแซกสองครั้ง)
- Wave 4 พัฒนาโดยทั่วไปว่าเป็นรูปแบบการแก้ไขที่ซับซ้อน (เช่นสามเหลี่ยมสอง / สามสามแบน)
- ในเกือบทุกแรงกระตุ้นคลื่นกระทำหนึ่ง (1,3 หรือ 5) ขยายออกไปและเป็นคลื่นที่พบมากที่สุด 3
- คลื่นที่ขยายอาจมีส่วนขยายเพิ่มเติมหลายรายการ
- คลื่น 5 สามารถล้มเหลวเกินกว่าคลื่น 3 (การตัด) แต่มันไม่ธรรมดา มันมักจะเกิดขึ้นเมื่อคลื่น 3 ยาวเป็นพิเศษและยืดเยื้อ การตัดมักส่งผลให้เกิดการพลิกกลับที่สำคัญ
- คลื่น 5 น่าจะไม่ก่อให้เกิดแนวทแยงถ้าคลื่น 3 ไม่ได้ยืดออก
- แรงกระตุ้นไม่จบจนกว่าองศาย่อยทั้งหมดจะเสร็จสิ้น (เช่น 5 จาก 5 ของ 5) การนับคลื่นจะมีความสำคัญเหนือเส้นของช่องทางและเป้าหมายของ Fibonacci
- Wave 3 มักแสดงปริมาณที่มากที่สุด หากไดรฟ์ในช่วง 5 วันที่คลื่นจะสูงถึง 3 ถคาดว่าขยาย 5 TH คลื่น
Fibonacci Retracement และแนวทางการขยาย:
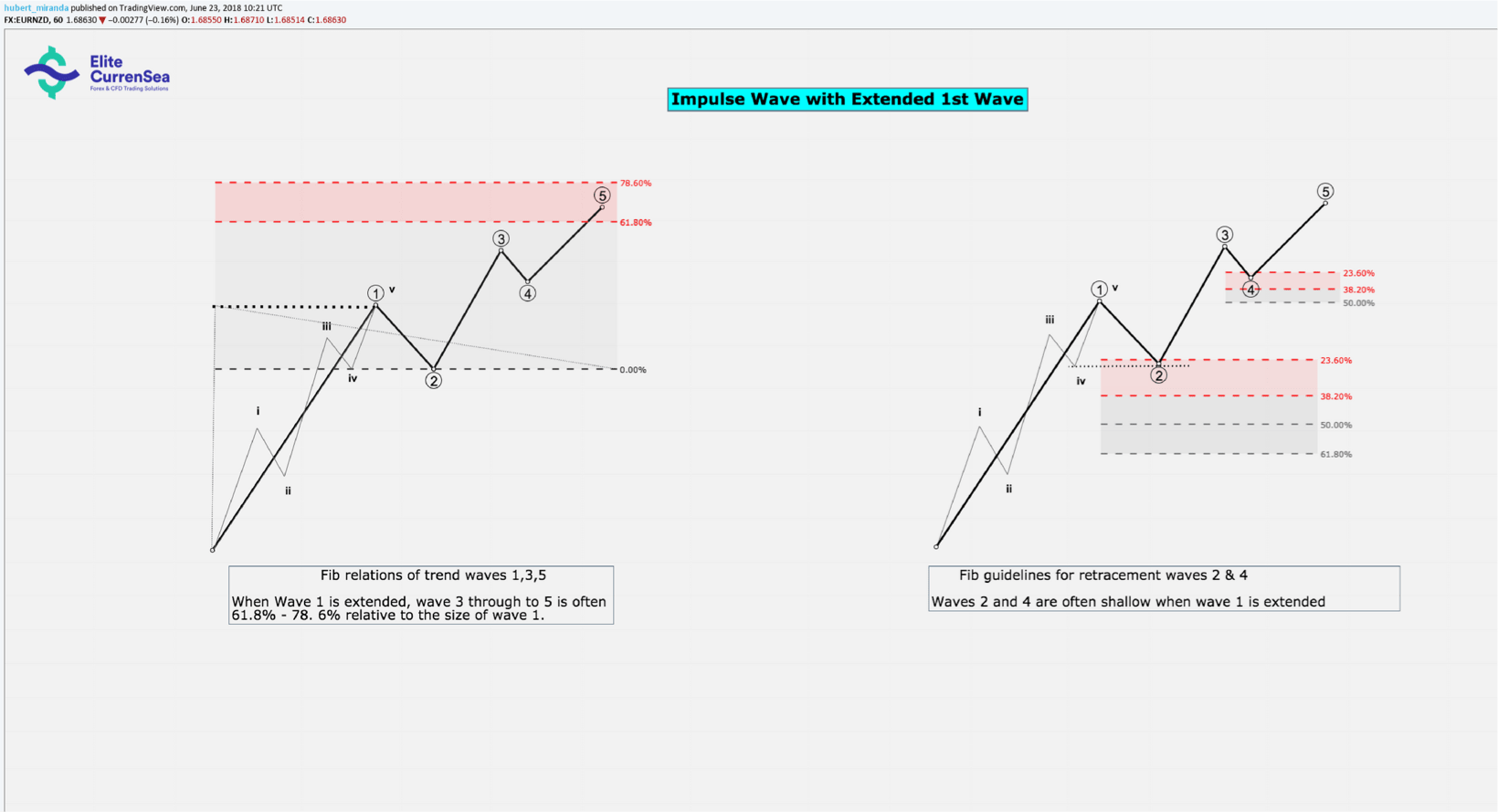
- หากคลื่น 1 ถูกขยายออกขนาดของคลื่น 3 ถึงจุดสิ้นสุดของคลื่น 5 มักจะ 61.8% - 78.6% เมื่อเทียบกับขนาดของคลื่น 1
- หากคลื่นที่ 1 ขยายออกไปคลื่นที่ 2 และ 4 จะมีความตื้นมาก (เช่น 23.6% - 38.2%)
- หากคลื่น 1 ถูกขยายออกไปคลื่นที่ 2 มักจะสิ้นสุดที่ระดับของคลื่นย่อย 4 ของ 1 (เช่นคลื่นภายใน 4 ของคลื่น 1)
- หากคลื่น 2 ตอบโต้มากกว่า 78.6% ของคลื่น 1 ความคิดที่ว่าคลื่น 2 จริง ๆ น่าสงสัยมากขึ้น (อาจเป็นไปได้ AB)
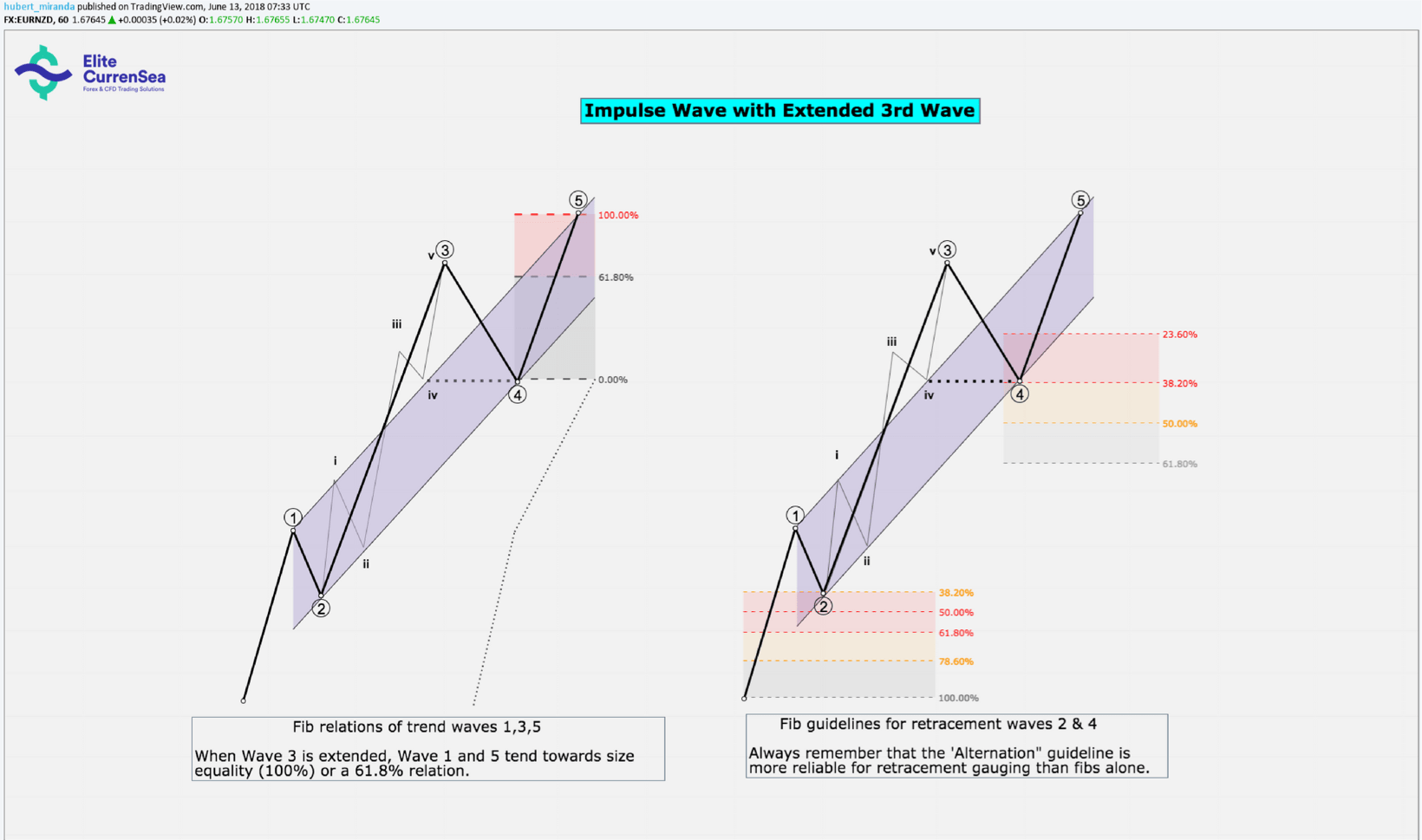
- หากคลื่น 3 ถูกขยายออกมาคลื่นที่ 1 และ 5 มักจะมีขนาดและระยะเวลาเกือบเท่ากัน หากขาดความเสมอภาคความสัมพันธ์ 61.8% เป็นไปได้มากที่สุด
- หากคลื่น 3 ถูกขยายออกไปคลื่น 4 มักจะสิ้นสุดที่ระดับของคลื่นย่อย 4 ของ 3 และค่อนข้างตื้น (retraces 23.6% - 38.2% ของคลื่น 3)
- หากคลื่น 3 ถูกขยายและแนวตั้งมากจะมีแนวโน้มที่จะเกินช่องแนวโน้มที่สามารถวาดเมื่อวางจุดยึดที่ปลายสุดของคลื่น 1, 2 และ 4 อย่างไรก็ตามช่องยังคงถูกต้องมากสำหรับการวัดจุดสิ้นสุดของคลื่น 5 (ดูภาพ)
- หากคลื่น 4 ตอบโต้มากกว่า 50% ของคลื่น 3 ก็มักจะไม่ใช่คลื่น 4
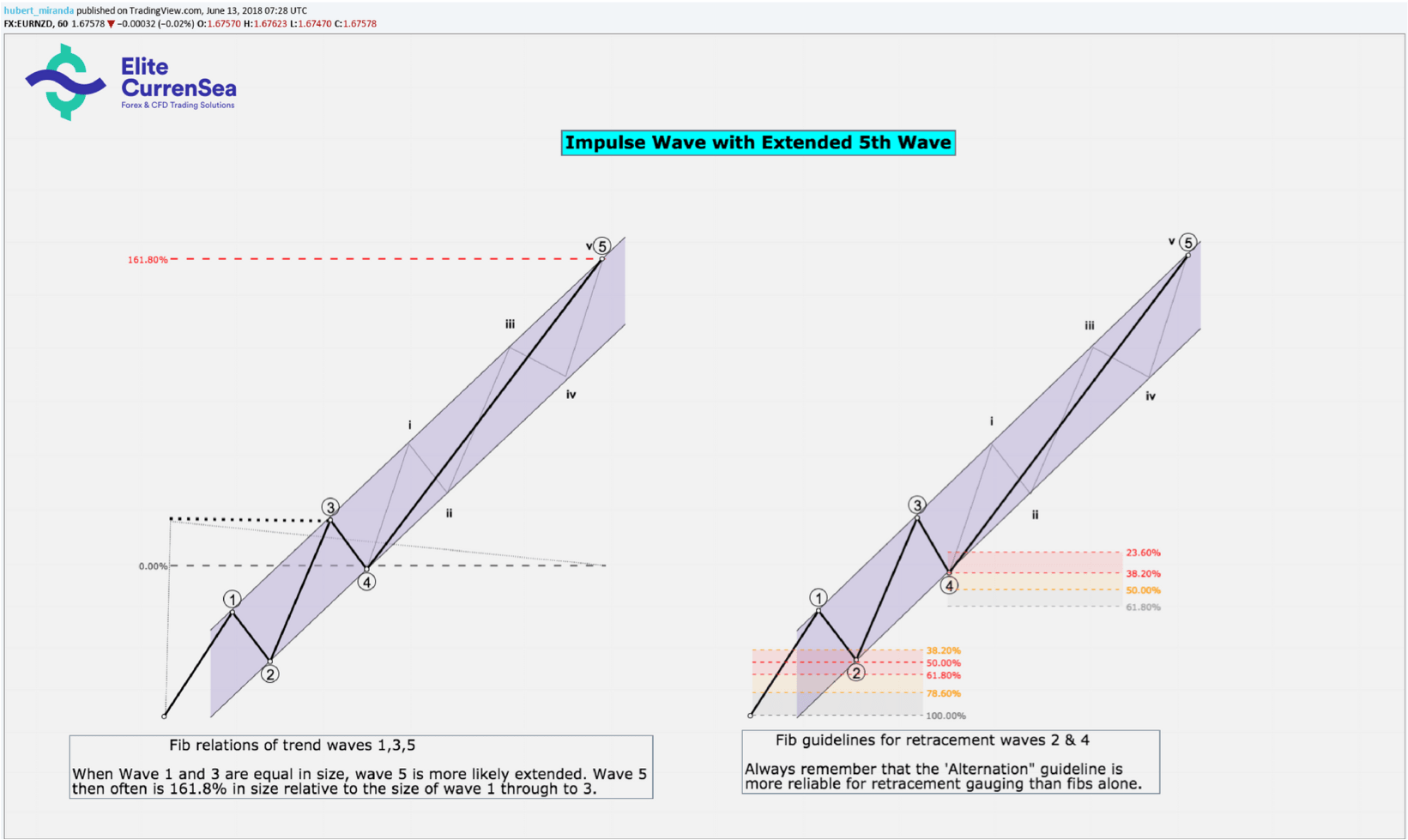
- คลื่น 5 มีแนวโน้มที่จะขยายออกไปหากคลื่น 1 และ 3 มีขนาดเท่ากัน
- หากคลื่น 5 ถูกขยายออกไปก็มักจะเสร็จสิ้นที่ส่วนขยาย 161.8% เทียบกับขนาดของคลื่น 1 ถึง 3 (ดูภาพ)
- หากคลื่น 5 ถูกขยายออกการแก้ไขที่ตามมามักจะคมชัดและรวดเร็วและสิ้นสุดลงใกล้กับคลื่นย่อย 2 ของการขยาย นี้ใช้ไม่ได้เมื่อตลาดกำลังจะสิ้นสุดลง 5 TH คลื่นพร้อมกันมากกว่าหนึ่งระดับ
Motive Wave: DIAGONAL
หมายเหตุ: เปอร์เซ็นต์ในข้างต้นสำหรับเป้าหมายการขยาย Fibonacci ถูกดึงจากจุดเริ่มต้นของคลื่น แต่อัตราส่วนจะขึ้นอยู่กับขนาดของคลื่นเคลื่อนที่ก่อนหน้า (เช่นเป้าหมายของ 3 จะสัมพันธ์กับขนาดของคลื่น 1 เป้าหมายของคลื่น 5 มีความสัมพันธ์กับขนาดของคลื่น 3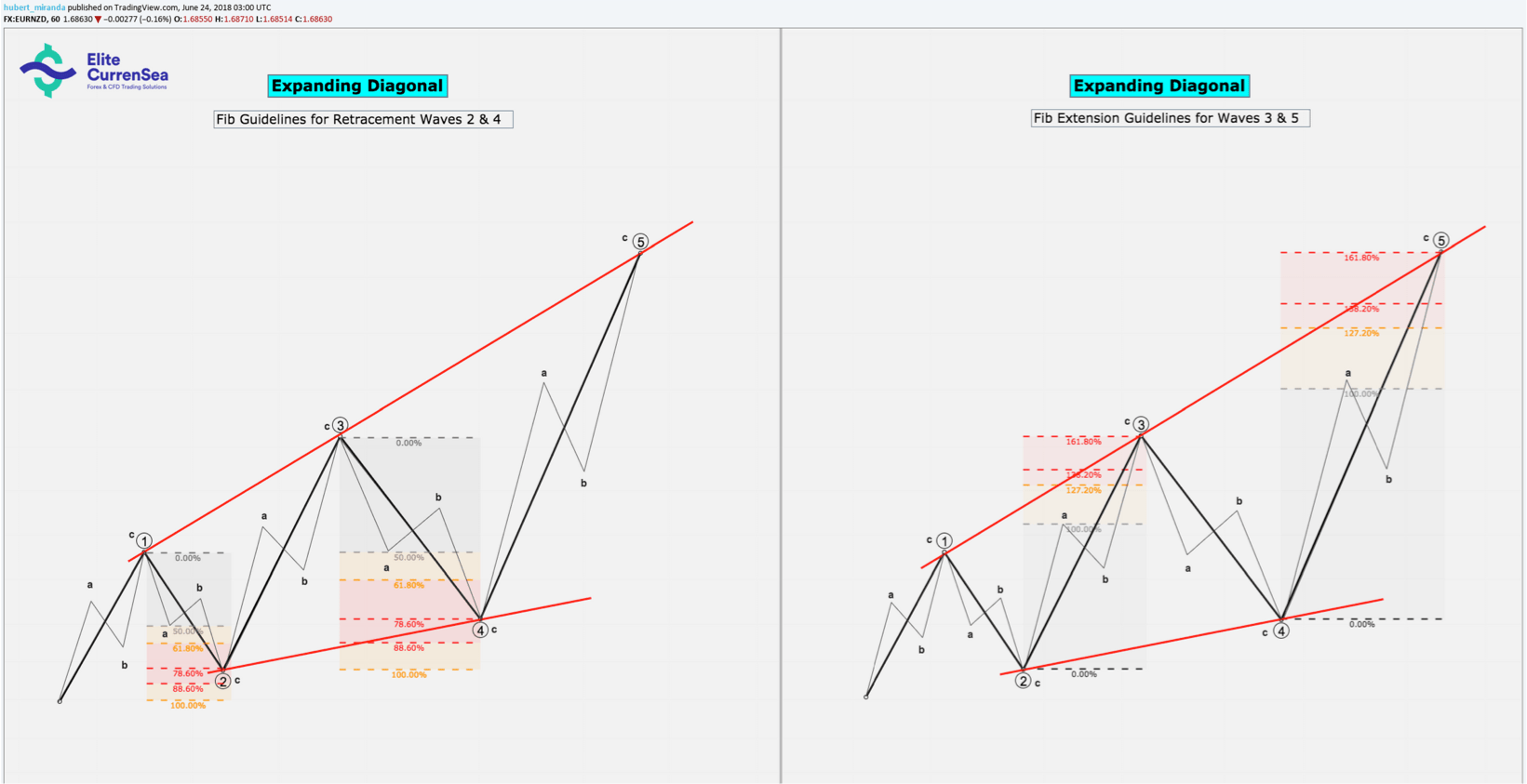

หมายเหตุ: เปอร์เซ็นต์ในข้างต้นสำหรับเป้าหมายการขยาย Fibonacci ถูกดึงจากจุดเริ่มต้นของคลื่น แต่อัตราส่วนจะขึ้นอยู่กับขนาดของคลื่นเคลื่อนที่ก่อนหน้า (เช่นเป้าหมายของ 3 จะสัมพันธ์กับขนาดของคลื่น 1 เป้าหมายของคลื่น 5 มีความสัมพันธ์กับขนาดของคลื่น 3
กฎ:
- เส้นทแยงมุมทั้งหมดประกอบด้วย 5 คลื่น
- เส้นทแยงมุมสามารถเป็น 'นำ' หรือ 'สิ้นสุด' เส้นทแยงมุมขึ้นอยู่กับว่าพวกเขาก่อตัวที่จุดเริ่มต้นหรือจุดสิ้นสุดของแนวโน้ม เส้นทแยงมุมสามารถเกิดขึ้นได้ในตำแหน่งของคลื่น 1 (นำ) หรือ 5 (สิ้นสุด) ของแรงกระตุ้นหรือตำแหน่งของคลื่น A (นำ) หรือ C (สิ้นสุด) ของซิกแซก
- ภายในเส้นทแยงมุมที่สิ้นสุดคลื่นทั้ง 5 ลูกจะต้องเป็นซิกแซก (แบบง่าย -, - และ - สาม - ซิกแซกทั้งหมด)
- ภายในแนวทแยงมุมชั้นนำอย่างน้อยคลื่นที่ 2 และ 4 จะต้องเป็นซิกแซก (แบบง่าย, แบบคู่, แบบสองครั้งและแบบสามชั้นแบบซิกแซกจะใช้ได้ทั้งหมด) คลื่น 1, 3 และ 5 อาจเป็นแรงกระตุ้นหรือซิกแซก (ถ้า 1, 3 และ 5 เป็นแรงกระตุ้นโปรดระวังว่ามันอาจเป็นลำดับ 1-2, 1-2, 1-2 ได้ง่ายแทนที่จะเป็นแนวทแยง)
- คลื่น 2 ต้องไม่ย้อนกลับเกิน 100% ของคลื่น 1
- Wave 4 ต้องทับซ้อนกับ wave 1 (โปรดทราบว่าความคิดเห็นที่แตกต่างไปจากกฎนี้มีนักวิจัยของ Elliott Wave บางคนที่เชื่อว่าการสิ้นสุดและ diagonals ชั้นนำสามารถใช้ได้โดยไม่ต้อง wave 4 จำเป็นต้องย้ายเข้าสู่ดินแดนของคลื่น 1 ที่ผิดปกติ)
- คลื่น 4 ไม่เคยเคลื่อนไหวเกินปลายคลื่น 2
- ชั้นนำและเส้นทแยงมุมขยายไม่ต้องมีการตัดทอน 5 TH คลื่น
- เส้นทแยงมุมการทำสัญญามีคลื่นที่สั้นกว่า 3 เสมอกว่า 1 คลื่น (ในแง่ของร้อยละกำไร / ขาดทุน)
- เส้นทแยงมุมทำสัญญามีคลื่นสั้น 5 เสมอกว่าคลื่น 3 (ในแง่ของร้อยละกำไร / ขาดทุน)
- เส้นทแยงมุมการทำสัญญาจะมีคลื่นที่สั้นกว่า 4 มากกว่าคลื่น 2 เสมอ (ในรูปของเปอร์เซ็นต์กำไร / ขาดทุน)
- เส้นทแยงมุมขยายตัวมีคลื่น 3 ยาวกว่าคลื่น 1 เสมอ (ในรูปของเปอร์เซ็นต์กำไร / ขาดทุน)
- เส้นทแยงมุมขยายตัวมีคลื่นอีกต่อไป 5 กว่าคลื่น 3 เสมอ (ในแง่ของร้อยละกำไร / ขาดทุน)
- เส้นทแยงมุมขยายตัวมีคลื่นยาวกว่า 4 เสมอ 2 คลื่น (ในแง่ของร้อยละกำไร / ขาดทุน)
แนวทาง:
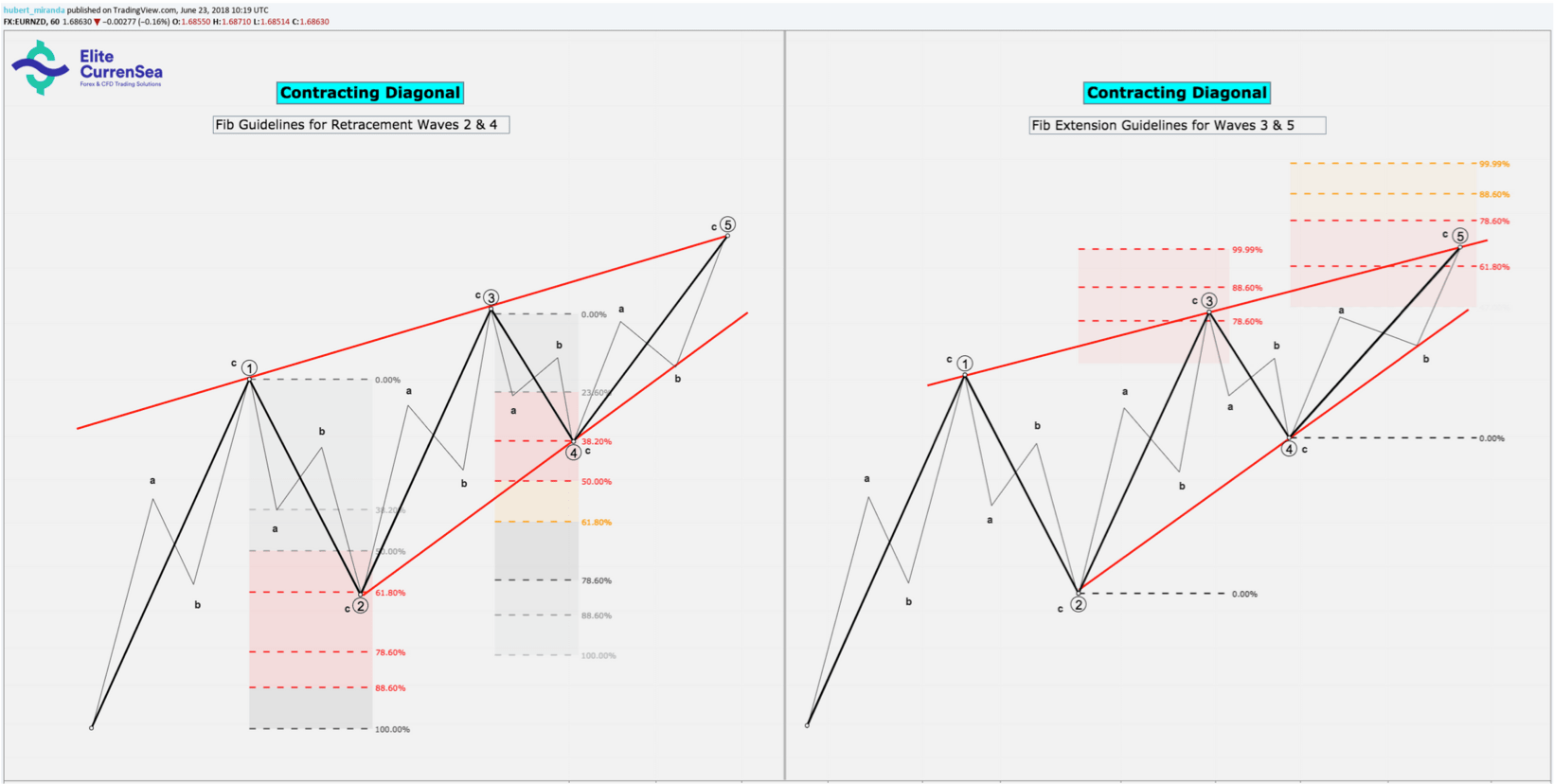
- การทำสัญญา diagonals เกิดขึ้นภายในเส้นแนวโน้มการรวมตัวสองเส้น (contracting wedge)
- เส้นทแยงมุมทำสัญญาสามารถเกินเส้นเทรนด์ในช่วงคลื่นที่ 5 (เรียกว่าการทุ่มตลาด) และยังคงใช้ได้ตราบใดที่คลื่น 5 ยังเล็กกว่าคลื่น 3
- การทำสัญญาเส้นทแยงมุมที่สิ้นสุดยังสามารถเพิ่มบรรทัดแนวโน้มในช่วงคลื่น 5 (การตัด)
- การหดตัวของเส้นทแยงมุมสิ้นสุดควรแสดงการลดลงของโมเมนตัมที่สอดคล้องกันเมื่อพวกเขาก้าวหน้าไปสู่จุดสูงสุด เทียนขนาดเล็กจำนวนมากที่ใช้เวลามากในการรับดินต่อไปนี้เป็นสัญญาณที่ดีว่ามีการสิ้นสุดแนวทแยงเกิดขึ้นจริง ในทางกลับกันแท่งเทียนขนาดใหญ่ที่มีความแข็งแกร่งในแนวทแยงที่มีศักยภาพควรเป็นสัญญาณเตือนว่าคุณน่าจะเห็นแนวโน้มที่ขยาย 1-2, 1-2, 1-2 และดังนั้นจึงไม่ใช่เส้นทแยงมุมที่สิ้นสุด
- การขยายรูป diagonals ภายในเส้นแนวโน้มแยกสองเส้น (ขยายลิ่ม) พวกมันหายากกว่าการทำสัญญาเส้นทแยงมุม
- คลื่น 2 และ 4 ของเส้นทแยงมุมใด ๆ มักจะย้อนกลับคลื่นของพวกเขา 1 และ 3 ลึกมากเมื่อเทียบกับคลื่น 2 และ 4 ของแรงกระตุ้น
- ซิกแซกภายในของเส้นทแยงมุมบางครั้งสามารถแบ่งออกเป็นซิกแซกสองเท่าหรือสามเท่าที่ซับซ้อนมากขึ้น
- เส้นทแยงมุมใด ๆ สามารถเริ่มได้รับการยืนยันด้วยความมั่นใจที่สูงขึ้นเมื่อคลื่น 4 ใกล้จะเสร็จสมบูรณ์
- โดยทั่วไปแล้ว Diagonals จะหายากกว่า (แม้ว่าจะเกิดขึ้นค่อนข้างบ่อยในคลื่นย่อยขององศาคลื่นขนาดเล็กมากที่สามารถมองเห็นได้ในช่วงเวลาของ M15 และต่ำกว่า)
- หากคลื่น 1 เป็นเส้นทแยงมุมนำคลื่น 3 มักจะยืดออก
- สถานที่ที่ควรระวังเส้นทแยงมุมชั้นนำที่มีศักยภาพกำลังขยายตัวอยู่ในช่วงเริ่มต้นของการลดลงของตลาดหุ้น เส้นทแยงมุมเกิดขึ้นเนื่องจากกองกำลังชั่วคราวของการเปลี่ยนแปลงแนวโน้มทำหน้าที่ซึ่งกันและกัน
- จุดจบของเส้นทแยงมุมจะตามมาด้วยการพลิกกลับที่แข็งแกร่งเกือบตลอดเวลา
คำแนะนำการใช้งาน Fibonacci Retracement และส่วนต่อขยาย: อ้างถึงรูปภาพสำหรับการปรับเปลี่ยนตำแหน่งและเป้าหมายส่วนขยาย
Corrective Wave: ZIGZAG
หมายเหตุ: เปอร์เซ็นต์ในข้างต้นสำหรับเป้าหมายการขยาย Fibonacci ถูกดึงจากจุดเริ่มต้นของคลื่น แต่อัตราส่วนจะขึ้นอยู่กับขนาดของคลื่นก่อนหน้าของทิศทางเดียวกัน (เช่นเป้าหมายของ C สัมพันธ์กับขนาดของคลื่น A เป้าหมายของคลื่น Y สัมพันธ์กับขนาดของคลื่น W เป้าหมายของคลื่น Z นั้นสัมพันธ์กับขนาดของคลื่น Y
กฎ:
- ซิกแซกประกอบด้วย 3 คลื่น (A, B และ C)
- คลื่น A ต้องเป็นแรงกระตุ้นหรือแนวทแยงมุม
- Wave C จะต้องมีแรงกระตุ้นหรือสิ้นสุดในแนวทแยง
- อนุญาตให้ใช้เส้นทแยงมุมหนึ่งเส้นเท่านั้น (A หรือ C) ต่อซิกแซกคือต้องมีแรงกระตุ้นอย่างน้อยหนึ่งจุด (A หรือ C)
- Wave B สามารถแก้ไขรูปแบบใดก็ได้ (ซิกแซก, แบน, สามเหลี่ยม, การรวมที่ซับซ้อน)
- Wave B ต้องไม่หวนกลับ Wave A มากกว่า 100%
แนวทาง:
- โดยปกติแล้วคลื่น C ควรอยู่เหนือกว่า A. คลื่น C สามารถถูกตัดทอนได้ (เช่นไม่ไปไกลกว่าคลื่น A) แต่มันหายากมาก
- คดเคี้ยวไปมาสามารถขยายเป็นสองเท่าหรือสองคดเคี้ยวไปมาในกรณีที่พวกเขาจะมีป้ายกำกับ wxy (คดเคี้ยวไปมาสองครั้ง) และ wxyz (ซิกแซกสาม) W, Y และ Z จะแบ่งย่อยเป็นซิกแซก ABC ของตัวเองในขณะที่ X wave / s สามารถเป็นรูปแบบการแก้ไขใด ๆ (พวกเขาทำหน้าที่เหมือนกับคลื่น B ในซิกแซกธรรมดา) คดเคี้ยวไปมามักจะเกิดขึ้นเมื่อคดเคี้ยวไปมาเรียบง่ายปรากฏขนาดเล็กเกินไปในแง่ของเวลาและขนาดเพื่อที่จะเป็นสัดส่วนกับการแกว่งซึ่งมันถูกแก้ไข
- ซิกแซกสามารถใช้รูปร่างและขนาดต่าง ๆ ได้ หนึ่งในคุณสมบัติที่สามารถช่วยแยกความแตกต่างของซิกแซก ABC ได้จากอิมพัลส์ 1-2-3 คือคลื่น A และ B นั้นจะทับซ้อนกันโดยทั่วไปและคลื่น A มักจะเสร็จเร็วกว่าคลื่น 1 ในแง่ของเวลาและขนาด คดเคี้ยวไปมามักจะแสดงช่องทางที่ลาดเอียงเบา ๆ ในขณะที่ 1-2-3 มักจะสูงชันมากขึ้น
Fibonacci Retracement และแนวทางการขยาย:
- คลื่น A และ C ของการแก้ไขมีแนวโน้มที่จะเท่าเทียมกัน (ขนาดเดียวกัน 100%) อัตราส่วนทั่วไปต่อไปคือ C = 161.8% x A หรือ C = 61.8% x A
- โดยปกติแล้วคลื่น B จะย้อนกลับระหว่าง 38% - 79% ของคลื่น A
- หากคลื่น B เป็นรูปสามเหลี่ยมจะมีโอกาสสูงกว่าที่คลื่น C อาจเข้าถึงเป้าหมายส่วนขยาย 61.8% เท่านั้น
- หากคลื่น B เป็นรูปสามเหลี่ยมที่กำลังวิ่งอยู่โดยทั่วไปแล้วจะย้อนกลับ 10 - 40% ของคลื่น A
- หากคลื่น B เป็นการแก้ไขด้านอื่น ๆ โดยทั่วไปจะเป็น 38% - 50% ของคลื่น A
- หากคลื่น B เป็นคดเคี้ยวไปมาโดยทั่วไปจะย้อนกลับ 50% - 79% ของคลื่น A
คลื่นแก้ไข: แบน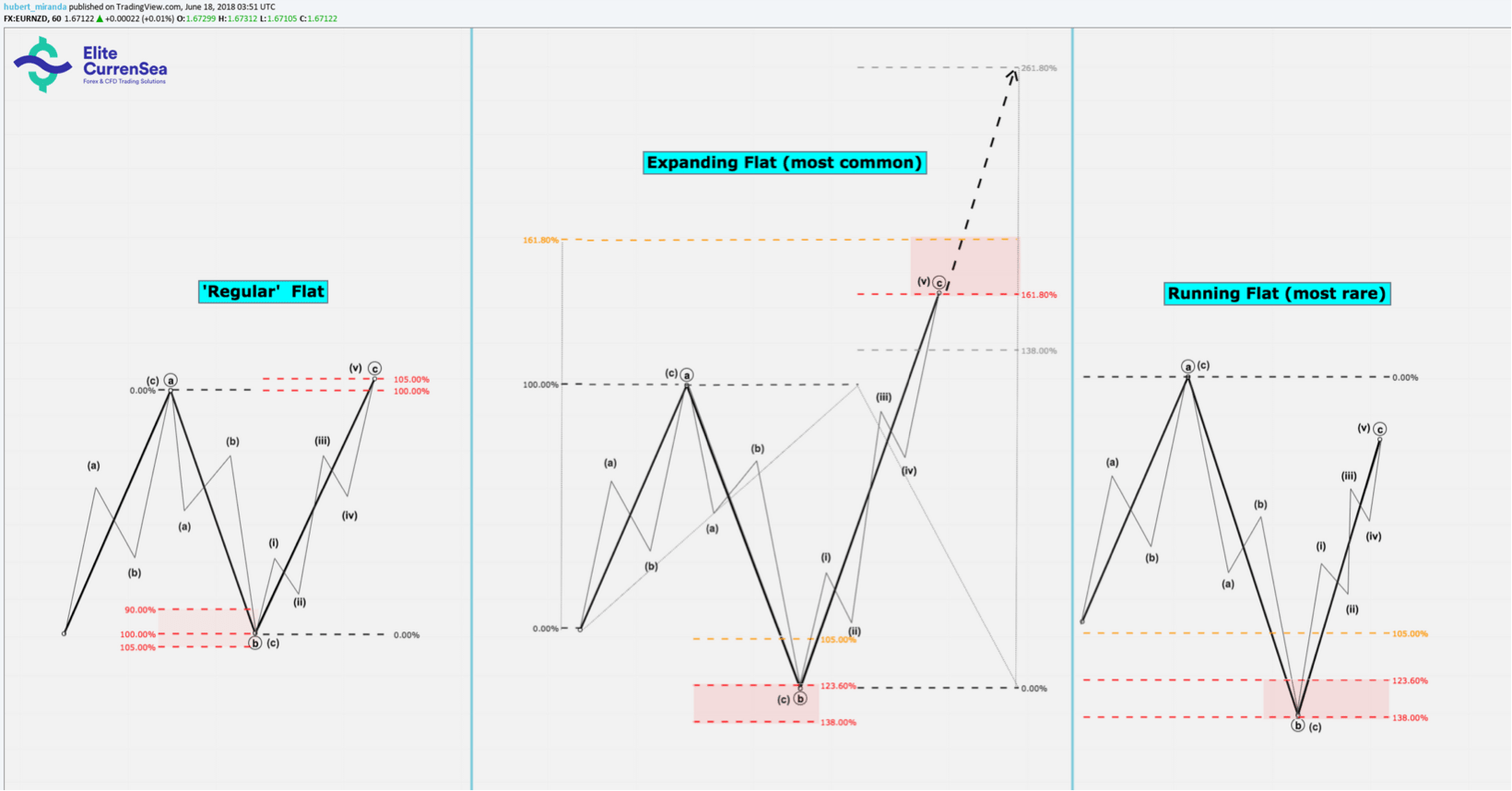
กฎ:
- แฟลตทั้งหมดประกอบด้วย 3 คลื่น (ABC)
- Wave A และ B ต้องแบ่งออกเป็นรูปแบบการแก้ไขใด ๆ แต่ Wave A ไม่สามารถเป็นรูปสามเหลี่ยมได้
- คลื่น C จะต้องเป็นคลื่นแรงจูงใจ (เช่นแรงกระตุ้นหรือเส้นทแยงมุม)
- Wave B ต้องย้อนกลับ wave A อย่างน้อย 90%
แนวทาง:
- โครงสร้างนี้เรียกว่า 'การขยาย' แบบเรียบถ้าคลื่น B retraces ระหว่าง 105% - 138% ของคลื่น A และคลื่น C สิ้นสุดที่ใดก็ตามที่เกินปลายคลื่น A การขยายตัวของแฟลตเกิดขึ้นบ่อยที่สุด
- โครงสร้างนี้เรียกว่า 'ปกติ' แบนหากคลื่น B ย้อนกลับไประหว่าง 90% - 105% ของคลื่น A และขนาดของคลื่น C คือ 100% - 105% ของคลื่น A แฟลตปกติเป็นของหายากมากกว่า
- โครงสร้างนี้เรียกว่า 'การวิ่ง' แบบเรียบถ้าคลื่น B จบลงจากจุดเริ่มต้นของคลื่น A แต่คลื่น C ล้มเหลวในการเข้าถึงเกินจุดสิ้นสุดของคลื่น A การใช้งานรองเท้าส้นเตี้ยนั้นหายากมากและการนับคลื่นทางเลือกอื่น ๆ เป็นรันแฟลตโดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่งในเครื่องชั่งขนาดใหญ่
- เมื่อใดก็ตามที่แรงกระตุ้น (แนวโน้ม) สิ้นสุดลงในสิ่งที่ดูเหมือนแกว่ง 3 คลื่นแล้วย้อนกลับอย่างรวดเร็วโปรดระวังว่ามันอาจจะขยายตัวแบนและทิศทางแนวโน้มเก่าอาจกลับมาทำงานทันที
Fibonacci Retracement และแนวทางการขยาย:
- อ้างถึงรูปภาพสำหรับการปรับปรุงหลักและเป้าหมายส่วนขยาย
- Wave C มักจะมีขนาด 100% - 161.8% x ขนาดของ Wave A แต่เป็นไปได้ที่จะมีขนาดใหญ่ถึง 261.8% ในโอกาสที่หายาก บางครั้งเป้าหมายของคลื่น C สามารถวัดได้โดยใช้จุดเริ่มต้นของ Wave A เป็นฐานสำหรับเป้าหมายส่วนขยาย 161.8% (แทนที่จะใช้จุดเริ่มต้นของคลื่น C เป็นฐาน) วิธีนี้สร้างระดับราคาแตกต่างกันเล็กน้อยและขยายพื้นที่เป้าหมายเล็กน้อย
คลื่นแก้ไข: สามเหลี่ยม
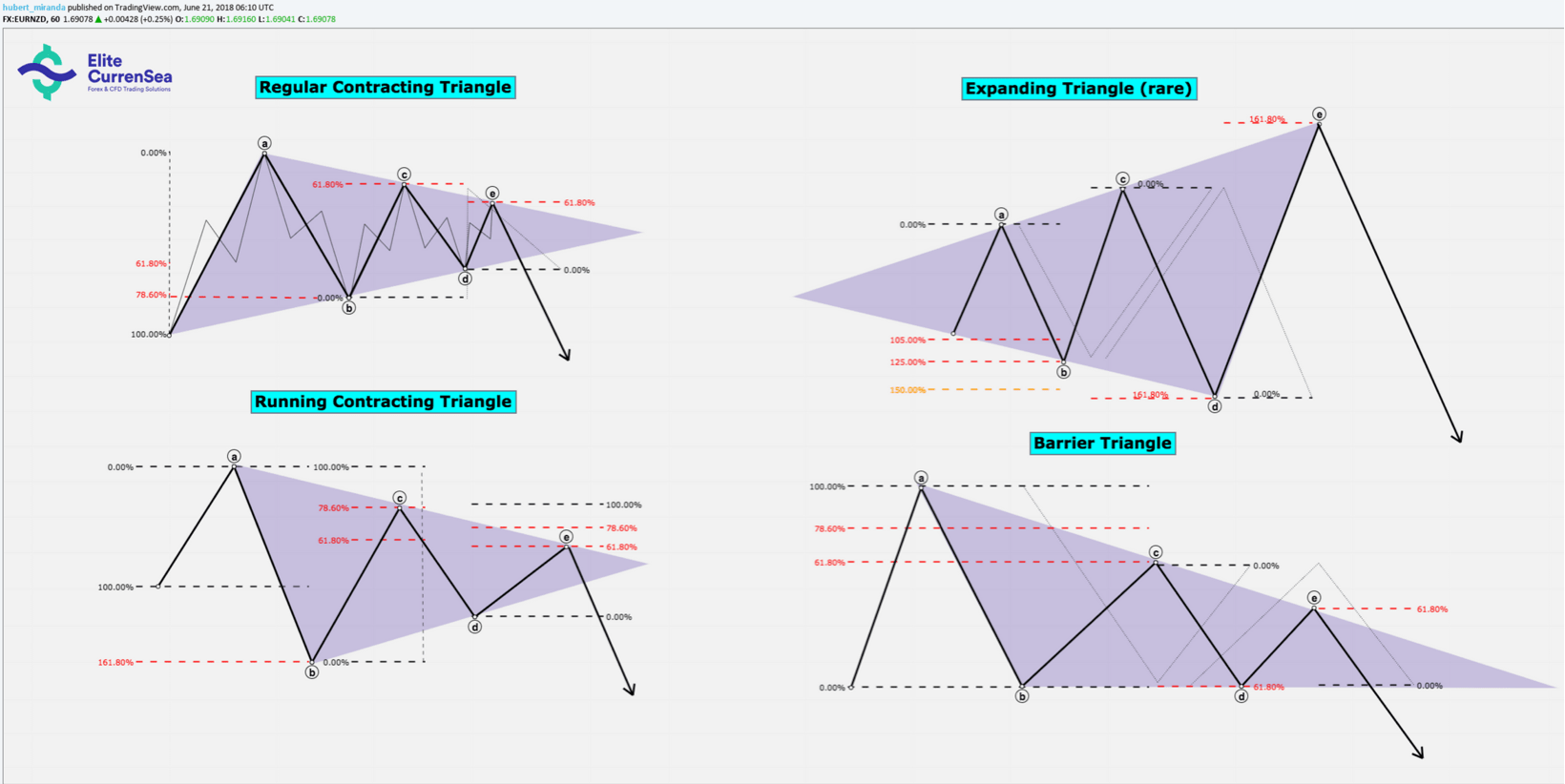 หมายเหตุ: โครงสร้างคดเคี้ยวไปมาภายในจะแสดงเฉพาะมันเป็นตัวอย่างสัญญาสามเหลี่ยมเพื่อหลีกเลี่ยงความยุ่งเหยิงของการวาดภาพที่มีเส้นมากเกินไป โปรดทราบว่าคลื่นทั้งหมดในรูปสามเหลี่ยมทั้งหมดประกอบด้วยรูปแบบคลื่นที่ถูกต้องแม้ว่าจะไม่ปรากฏในรูปภาพก็ตาม
หมายเหตุ: โครงสร้างคดเคี้ยวไปมาภายในจะแสดงเฉพาะมันเป็นตัวอย่างสัญญาสามเหลี่ยมเพื่อหลีกเลี่ยงความยุ่งเหยิงของการวาดภาพที่มีเส้นมากเกินไป โปรดทราบว่าคลื่นทั้งหมดในรูปสามเหลี่ยมทั้งหมดประกอบด้วยรูปแบบคลื่นที่ถูกต้องแม้ว่าจะไม่ปรากฏในรูปภาพก็ตาม
กฎ:
- รูปสามเหลี่ยมประกอบด้วย 5 คลื่นแก้ไข (ABCDE)
- รูปสามเหลี่ยมสามารถปรากฏในตำแหน่งของคลื่น 4 ของแรงกระตุ้น, คลื่น B / X ของซิกแซกและแฟลต, คลื่น Y ของการแก้ไขสองด้านสามคู่หรือคลื่น Z ของการแก้ไขสามด้านสาม
- อย่างน้อย 4 จาก 5 คลื่นแบ่งเป็นซิกแซก
- รูปสามเหลี่ยมไม่เคยมีคลื่นเชิงซ้อนมากกว่าหนึ่ง คลื่นที่สลับซับซ้อนภายในรูปสามเหลี่ยมสามารถเป็นรูปซิกแซกคู่หรือรูปสามเหลี่ยมได้
- ในการทำสัญญา & สิ่งกีดขวางสามเหลี่ยมคลื่น C ไม่เคลื่อนที่เกินคลื่น A, คลื่น D ไม่เคลื่อนที่ไปเหนือคลื่น B และคลื่น E ไม่เคลื่อนที่เกินคลื่น C ซึ่งส่งผลให้เกิดการรวมตัวกันของเส้นแนวโน้มสองเส้น ความแตกต่างที่สำคัญระหว่างสามเหลี่ยมกั้นคือสร้างเส้นแนวโน้มแนวนอนระหว่างจุด B และ D
- ในรูปสามเหลี่ยมที่ขยายตัวคลื่น B, C, D และ E ต้องย้อนกลับอย่างน้อย 100% ของคลื่นก่อนหน้า แต่ไม่เกิน 150% ซึ่งส่งผลให้เส้นแนวโน้มเบี่ยงเบนสองเส้นเกิดขึ้นเมื่อสามเหลี่ยมดำเนินไป
แนวทาง:
- ในรูปสามเหลี่ยมที่หดตัวคลื่น B สามารถสิ้นสุดได้ไกลกว่าจุดเริ่มต้นของคลื่น A (ประมาณ 60% ของเวลา) โครงสร้างนั้นเรียกว่า'Contracting Triangle' (ดูรูป)
- Wave E มีแนวโน้มค่อนข้างที่จะทำการ Undershoot หรือเกินเส้นแนวโน้มสามเหลี่ยม นี่เป็นปกติ.
- การขยายสามเหลี่ยมและสามเหลี่ยมกีดกันนั้นหาได้ยากกว่าการหดสามเหลี่ยม
- บ่อยครั้งที่หนึ่งในคลื่นกลายเป็นซับซ้อน มันมีแนวโน้มที่จะเป็นคลื่น C หรือ D ที่กลายเป็นคดเคี้ยวไปมาที่ซับซ้อน (สอง / สาม) บางครั้งคลื่น C, D, หรือ E เปลี่ยนเป็นอุปสรรคหรือทำสัญญาสามเหลี่ยมด้วยตัวเอง หากคลื่นสุดท้าย E เปลี่ยนเป็นรูปสามเหลี่ยมโครงสร้างทั้งหมดจะขยายเป็น 9 คลื่นซึ่งแคบลงกว่าเดิม สามเหลี่ยมนั้นจะได้รับการระบุว่าเป็น ABCDEFGHI
- ในระหว่างการทำสัญญาและสามเหลี่ยมกีดขวางโมเมนตัมและปริมาณลดลง
- โดยปกติจะมีแรงขับ (คลื่น 5) โพสต์รูปสามเหลี่ยมหลังจากคลื่น E เสร็จสิ้นซึ่งจะมีขนาดเท่ากับความกว้างของเส้นแนวโน้มที่จุดเริ่มต้นของรูปสามเหลี่ยม
- แรงขับของโพสต์รูปสามเหลี่ยม (wave 5) ในสินค้าโภคภัณฑ์มักเป็นคลื่นที่ยาวที่สุดของแนวโน้มทั้งหมด
Fibonacci Retracement และแนวทางการขยาย:
- ในรูปสามเหลี่ยมเกร็งหรือสิ่งกีดขวางคลื่นจำนวนมากมีความสัมพันธ์ 61.8% - 78.6% กับคลื่นก่อนหน้าหรือคลื่นสลับ
- ในการใช้รูปสามเหลี่ยมสามเหลี่ยมคลื่น B ควรกลับคืนคลื่น A ไม่เกิน 161.8%
- ในสามเหลี่ยมกำลังขยายคลื่น C มักจะเป็น 161.8% ของคลื่น A คลื่น D เป็น 161.8% ของคลื่น B และคลื่น E คือ 161.8% ของคลื่น C
- ดูภาพเพื่อดูรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติม
คลื่นแก้ไข: คอมเพล็กซ์รวม
(โปรดทราบว่าชุดค่าผสมของ ZigZag ที่ซับซ้อนได้รับการคุ้มครองภายใต้หัวข้อ Zigzag ก่อนหน้านี้ส่วนต่อไปนี้เกี่ยวข้องกับชุดค่าผสมที่ซับซ้อนด้านข้างเท่านั้น)
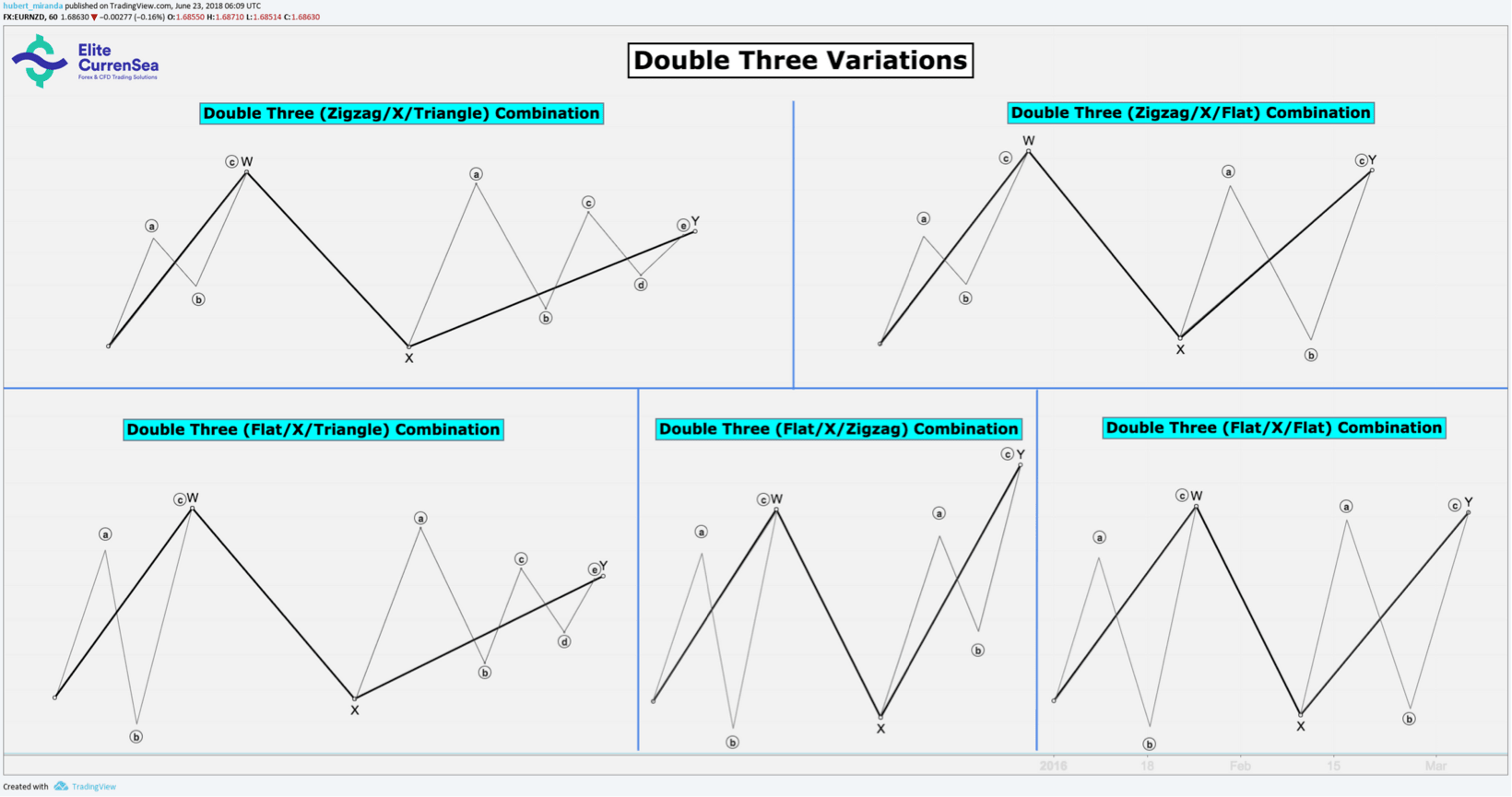
- การรวมกันด้านข้างที่ซับซ้อนประกอบด้วยสามหรือห้ารูปแบบการแก้ไขซึ่งสลับกันในทิศทางของพวกเขาดังนั้นจึงสร้างการเคลื่อนไหวด้านข้างที่ซับซ้อน รูปแบบการแก้ไขที่เป็นศูนย์กลางการหาร (คลื่น X) จะปรับทิศทางไปตามทิศทางของแนวโน้มที่สร้างไว้ก่อนหน้านี้เสมอ ดังนั้นชุดค่าผสม 'สองสาม' จึงประกอบด้วย 3 รูปแบบการแก้ไข (WXY) ในทิศทางสลับกันและการรวมกัน 'สามสาม' ประกอบด้วย 5 รูปแบบการแก้ไข (WXYXZ) ในทิศทางสลับกัน
- สองสามสามารถมีการแก้ไขดังต่อไปนี้:
- ซิกแซก (W), คลื่นแก้ไขใด ๆ (X) และแบน (Y)
- ซิกแซก (W), คลื่นแก้ไขใด ๆ (X) และสามเหลี่ยม (Y)
- แบน (W) แก้ไขคลื่นใด ๆ (X) และสามเหลี่ยม (Y)
- แบน (W), คลื่นแก้ไขใด ๆ (X), และแบน (Y)
- แบน (W), คลื่นแก้ไขใด ๆ (X) และซิกแซก (Y)
- Double Threes อนุญาตให้มีซิกแซกได้สูงสุดหนึ่งอันและหนึ่งสามเหลี่ยมในตำแหน่ง W และ Y แต่คลื่น X สามารถใด ๆ รูปแบบการแก้ไขนอกจาก(รวมถึงสองหรือสามสามรวมกันของระดับขนาดเล็ก!)
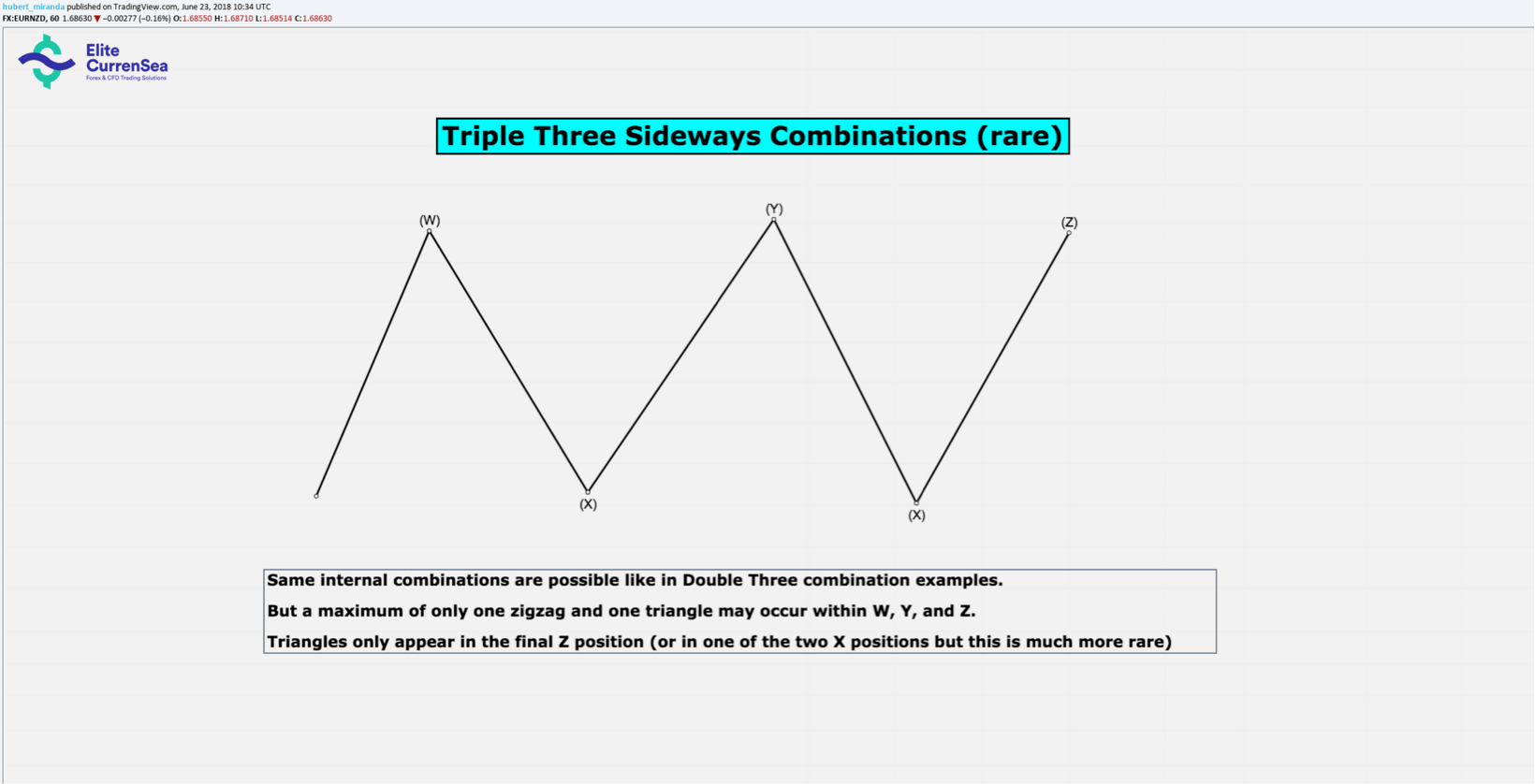
- Triple Three ทำงานในลักษณะเช่นเดียวกับสามคู่และก็ยังได้รับอนุญาตเท่านั้นที่จะมีหนึ่งคดเคี้ยวและเป็นหนึ่งในสามเหลี่ยม W, Y, Z และตำแหน่ง คลื่น X ในสามสามสามารถเป็นรูปแบบการแก้ไขเพิ่มเติมใด ๆ ( รวมถึงการรวมกันสองหรือสามสามของระดับเล็ก!)
- สามเหลี่ยมได้รับอนุญาตให้สร้างในคลื่นสุดท้ายของลำดับการรวมกัน (เช่นใน Double-Three ระหว่าง Wave Y หรือ Triple สามระหว่าง Wave Z)
- หมายเหตุสำคัญ: ความคิดเห็นที่แตกต่างกันระหว่างนักวิจัยของ Elliott Wave ว่าคลื่น W, Y และ Z ได้รับอนุญาตให้รวมกันที่ซับซ้อนภายในตัวเองได้หรือไม่ (เช่น wxy ขนาดเล็กภายใน W และอื่น ๆ ) งานวิจัยต้นฉบับแสดงให้เห็นว่า W, Y และ Z แต่ละคนจะต้องสามารถแบ่งออกเป็นรูปแบบการแก้ไขอย่างง่าย (เช่นคดเคี้ยวไปมาแบนหรือสามเหลี่ยม) ในระดับที่เล็กกว่าต่อไปและมีเพียงคลื่น X เท่านั้นที่จะแตกหน่อชุดเล็ก ภายในตัวเอง อย่างไรก็ตามนักวิเคราะห์สมัยใหม่บางคนเสนอว่าพฤติกรรมของตลาดมีความซับซ้อนมากขึ้นในทุกวันนี้และกำลังตรวจสอบความถูกต้องของการแก้ไขฉลากที่ซับซ้อนน้อยลงใน W, Y และ Z เช่นกันโดยส่วนตัวแล้วฉันยังไม่พบการใช้งานใด ๆ โดยการเพิ่มความซับซ้อนของคลื่น W, Y และ Z ในทางกลับกันฉันได้พบว่ามันสามารถนำไปสู่ 'การติดฉลากเกินพิกัด' ของการแก้ไขและทำให้เกิดการพิจารณาผิดในการเริ่มต้น ของแนวโน้มความต่อเนื่องหรือเป้าหมายการแก้ไข หากคุณเริ่มต้นด้วยคลื่น Elliott ฉันอยากจะแนะนำให้อยู่กับกฎเดิมที่ W, Y และ Z ควรจะสามารถแบ่งออกเป็นรูปแบบการแก้ไขง่ายๆ
แนวทาง:
- Triple Threes นั้นหายากมากเมื่อเทียบกับ Double Threes
- แม้ว่าในทางทฤษฎีแล้วคลื่น X อาจเป็นรูปสามเหลี่ยมได้นอกเหนือจากรูปสามเหลี่ยมในคลื่นสุดท้ายของการรวมกัน แต่ก็ไม่เคยเกิดขึ้นและมีแนวโน้มที่จะไม่เกิดขึ้นเพียงเพราะการเปลี่ยนแปลงของตลาด ดังนั้น Y หรือ Z สุดท้ายนั้นแทบจะไม่เคยเป็นสามเหลี่ยมอีกเลยถ้าX-wave เป็นรูปสามเหลี่ยมอยู่แล้ว
- การขยายรูปสามเหลี่ยมนั้นหาได้ยากมากในชุดค่าผสมที่ซับซ้อนและอาจไม่เคยมีใครเห็นมาก่อน
Fibonacci Retracement และแนวทางการขยาย:
- การรวมกันด้านข้างเป็นไปตามช่วงธรรมชาติที่ถูกผูกไว้ โดยทั่วไปคลื่นทั้งหมดจะย้อนกลับไปหากันประมาณ 78% - 138% ซึ่งเป็นการสร้างการเคลื่อนไหวในแนวนอนหรือช่องที่ค่อย ๆ ลาดเอียงไปตามทิศทางแนวโน้มก่อนหน้า
คู่มือสร้างและรวบรวมโดย Hubert Miranda ติดตามบน Twitter: @miranda_hubert